Abstract
Background
The FLT3 gene encodes a transmembrane receptor normally expressed by hematopoietic stem or progenitor cells that when mutated plays a role in the development of AML. Mutations in FLT3 are found in ~ 30% of newly diagnosed AML cases and primarily occur as internal tandem duplication (ITD) within the juxtamembrane domain (JMD) of the receptor (~ 25%) or point muts in the tyrosine kinase domains (TKD; 7-10%). Recently, point muts in the JMD have been identified as additional recurrent events. The JMD has an auto-inhibitory role preventing dimerization of FLT3 receptor, and disruption of this key region, whether by ITD or point mutation, is expected to result in constitutive activation of FLT3 receptor. However, thus far little is known about the biologic and clinical significance of FLT3-JMD.
Methods
To evaluate biologic and prognostic impacts of FLT3-JMD muts, we analyzed 1658 patients (pts) with newly diagnosed de novo AML treated similarly on frontline CALGB/Alliance protocols. All pts underwent high-throughput sequencing analysis of 80 AML-associated genes including FLT3 JMD and TKD regions, enabling FLT3-JMD variant curation. Survival analyses were conducted for pts with JMD present at ≥5% variant allele frequency (VAF). We tabulated distinct JMD muts and produced expression constructs for a subset of these. FLT3-JMD constructs were lentivirally transduced into Ba/F3 cells and cell growth was assessed over 7 days in the absence of interleukin 3 (IL-3). The analyses of the effect of FLT3 inhibitors on signaling and cell viability were done using MTT assays to evaluate the sensitivity of FLT3-JMD muts to available treatment options.
Results
We identified 44 point muts and deletions within FLT3-JMD in 39 pts, a prevalence of 2.4%. Most common were amino acid exchanges at residue V592 (D/A/I; n=10), followed by Y597C/*/del (n=4). JMD alterations frequently co-occurred with FLT3-ITD and TKD muts: of 39 pts, 26 (67%) also had ITD and 11 (28%) also had TKD. NPM1, RUNX1 and ASLX1 were the most frequently co-mutated genes.
Considering pts with VAF ≥5% (n=29), relapse rate (RR) was similar (62 vs 48%, p=0.55) but disease-free survival (DFS) trended shorter (median, 1.8 vs 2.4 y, p=0.07) in pts having FLT3-JMD with or without TKD (n=16) vs pts with TKD alone (n=124; p<.001), while both did significantly better than pts bearing ITD (RR 73%, DFS, median, 0.6 y). Despite this, median overall survival of pts with FLT3-JMD±TKD was 3.4 y compared to 1.7 y in FLT3-TKD only, although no significant difference existed at 5 y (44 vs 37%, p=0.19).
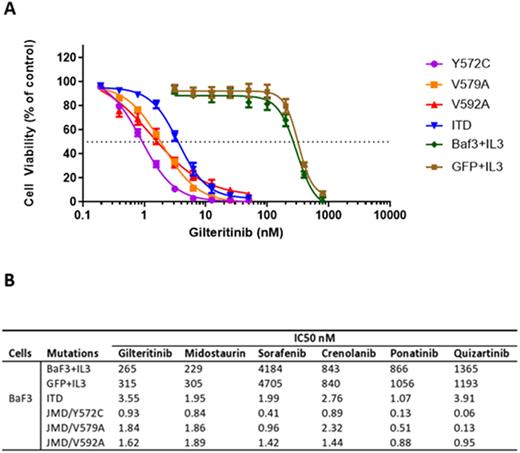
To complement these observations and explore biologic consequences of FLT3-JMD muts, we evaluated the transforming potential of the most frequent JMD muts in Ba/F3 cells, and their sensitivity to a panel of approved and clinical candidate FLT3 inhibitors in cell survival and signaling assays. Point muts in the FLT3-JMD were found to have transforming potential, because Ba/F3 cells expressing Y572C, V579A and V592A in the FLT3-JMD were able to grow in the absence of IL-3. Cell survival assays revealed that FLT3-JMD point muts can be targeted by available FLT3 inhibitors. Compared with FLT3-ITD, Y572C, V592A and V592A conferred high sensitivity to gilteritinib (Fig. 1A), in addition to a panel of available FLT3 inhibitors (Fig. 1B). Notably, JMD muts were also sensitive to quizartinib and sorafenib, whereas TKD muts are not.
Discussion
We analyzed a new and relatively understudied class of activating FLT3 muts clustering in the JMD and having outcome and treatment implications. Occurrence of JMD overall is rare, and co-occurrence with other FLT3 alterations is common, complicating dissection of outcomes. Patient data in a large historical dataset suggest that outcomes of pts with FLT3-JMD are similar to those with TKD, although with the possibility of higher RR and shorter DFS. Their median OS appeared longer than that of pts with TKD alone, but with no OS difference at later timepoints. These findings, if corroborated by larger studies, suggest distinct relapse dynamics. In vitro, the most common FLT3-JMD point muts confer a transforming potential to hematopoietic cells as predicted, and our data suggest that pts carrying FLT3-JMD point muts could respond to treatment with available FLT3 inhibitors. Finally, in contrast to TKD, JMD mutant cells are sensitive to type 2 FLT3 inhibitors, expanding the scope of treatment options for these pts.
Disclosures
Powell:Ambit Biosciences: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Hoffman LaRoche: Research Funding; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Rafael Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Research Funding. Baer:Kite, a Gilead Company: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Forma: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; Kura Oncology: Research Funding; Ascentage: Research Funding. Byrd:Janssen: Consultancy; Kura: Consultancy; Newave: Consultancy; Syndax: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Vincerx: Consultancy, Current equity holder in private company, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company; Zencor: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Research Funding; Ohio State University: Patents & Royalties; AbbVie: Consultancy; Trillium: Consultancy. Stock:Agios: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria; Kite: Honoraria; Kura Oncology: Honoraria; MorphoSys: Honoraria; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pluristem: Consultancy, Honoraria; Servier: Honoraria; Syndax: Consultancy, Honoraria; Newave Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Eisfeld:Karyopharm Therapeutics: Other: Spouse is current company employee. Blachly:KITE Pharma: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; INNATE Pharma: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MingSight Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.